
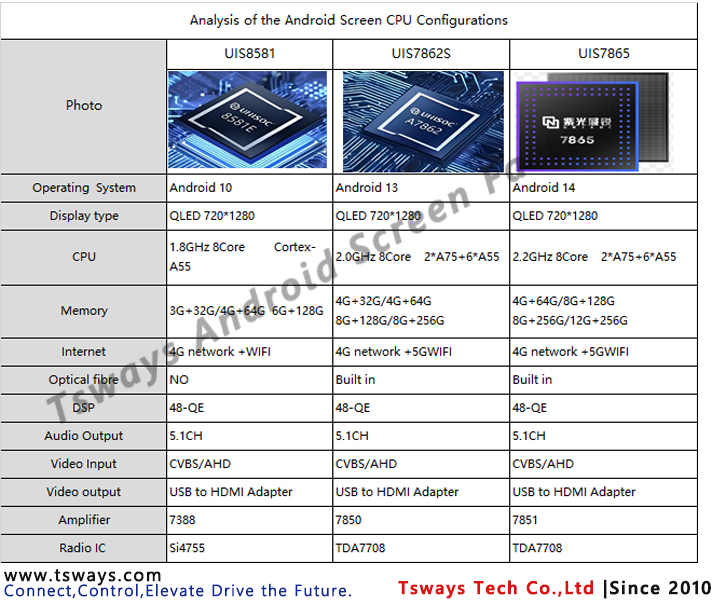
Unisoc 8581/7862S/7865 Chip Analysis
Unigroup Unisoc SC9863A (8581)
Official model number: The official model number for this chip is Unisoc SC9863A.
Origin of ‘8581’: This designation functions more as a project codename or a colloquial moniker for ease of recall and dissemination. In official technical documentation and product launches, Unisoc consistently refers to it as SC9863A. However, numerous solution providers, manufacturers, and e-commerce platforms commonly label it as ‘8581’ in their product descriptions.
Below is a detailed introduction to the Unigroup Unisoc SC9863A (8581) chip.
Key Technical Specifications
Process Technology: Employed a 28nm HKMG process technology, which at the time represented a mature solution offering an excellent balance between performance and power consumption.
CPU Architecture:
An octa-core CPU utilising Arm’s ‘big.LITTLE’ architecture.
Big cores: Four Arm Cortex-A55 cores, clocked up to 1.6 GHz.
Little cores: Four Arm Cortex-A55 cores, clocked up to 1.2 GHz.
Note: All cores are A55 variants, differing from higher-end chips (e.g., those combining A76/A75 big cores with A55 little cores). This clearly positions the chip as prioritising power efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Employing Unisoc’s SC9863A (8581) chipset—originally designed for entry-level smartphones—as the primary controller for in-vehicle infotainment systems represents a quintessential “cost-first” solution.
Disadvantages (Weaknesses and Risks) – This is the primary aspect requiring consideration
1. Severe performance shortcomings:
Weak CPU/GPU performance: The A55 cores and PowerVR GE8322 now appear significantly underpowered. In-car systems must simultaneously handle multiple tasks (such as navigation, music playback, Bluetooth calls, reversing camera feeds, and background system updates), while potentially supporting multi-screen displays. The SC9863A will suffer from pronounced lag, resulting in a profoundly poor user experience.
2. Disadvantages in Multimedia and Display Capabilities:
· Maximum support for only HD+ (720p) resolution: Mainstream in-vehicle infotainment systems now commonly feature 1080p or even higher resolutions. Displaying high-definition maps on a 720p screen would lack detail, potentially resulting in blurred text, significantly compromising readability and safety.
· Limited video decoding capability: Supports only 1080p@30fps video decoding, making it difficult to smoothly play back higher-definition dashcam footage or high-end reverse camera video streams.
3. Automotive Certification and Reliability:
· Non-automotive-grade chip: The SC9863A is a commercial-grade chip, not an automotive-grade chip. This means it has not undergone stringent AEC-Q100 certification and cannot meet the rigorous requirements of automotive applications in terms of operating temperature range (-40°C to 85°C or even higher), anti-interference capability, long-term stability, and lifespan. In extremely cold or hot environments, the system may fail, posing a significant safety risk.

Chip Overview: Tangula T740 (Unigroup 7862S)
The Unisoc T740 (commercially known as Unisoc 7862S) is a chip specifically designed for 5G smart terminals, with its design and optimization primarily targeting devices such as smartphones, tablets, and CPEs, rather than automotive-grade applications.
This fundamentally differs from the previously analyzed SC9863A (8581). The T740 offers significantly superior performance, but its suitability for in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems still requires a balanced perspective.
Chip Overview: Tangula T740 (Unisoc 7862S)
- Official Model: Unisoc Tangula T740 (Tiger T740).’7862S’ is one of its commercial codes.
- Process Technology: Utilizes 12nm EUV FinFET advanced process,offering relatively high power efficiency.
- CPU Architecture: Octa-core CPU consisting of four Arm Cortex-A75big cores (2.0GHz) and four Arm Cortex-A55 little cores (1.8GHz). This isa typical flagship-level big.LITTLE architecture, delivering performancefar exceeding that of previous A55 octa-core designs.
- GPU: Integrates an Imagination PowerVR GM9446 GPU,significantly enhancing graphics processing capabilities.
· Key Highlight: Features an integrated 5G modem supporting NSA/SA dual-mode 5G networks and Sub-6GHz bands, with a downlink peak rate of up to 3.25Gbps.
· AI: Equipped with an NPU (Neural Processing Unit) providing basic AI computing power, enabling applications such as facial recognition and voice wake-up.
· Multimedia: Supports up to 4K@30fps video encoding/decoding and display output with a maximum resolution of 2520×1080 (FHD+).
Analysis of Advantages and Disadvantages as an In-Vehicle Infotainment System Master Control
Advantages (Strengths)
1. Powerful Comprehensive Performance
o Sufficient CPU Performance: The A75+A55 architecture provides robust general computing capabilities, which are sufficient to smoothly run complex in-vehicle operating systems (e.g., Android Automotive OS, customized Android), Amap/Baidu Map Auto Edition, and multiple third-party applications (music, video, audiobooks, etc.) running simultaneously in the background, ensuring a smooth and stutter-free system experience.
o Enhanced GPU Performance: The PowerVR GM9446 can drive FHD+ (or even higher) resolution screens and render more sophisticated and complex UI animations and menu effects, offering a user experience far superior to entry-level chips.
2. Advanced 5G Connectivity
o High-Speed, Low-Latency Network: This is one of its greatest advantages. 5G connectivity enables ultra-fast OTA upgrades, high-quality online music/video streaming, real-time online navigation (with extremely quick traffic updates), and the potential to support future V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) applications, laying the foundation for ‘smart connected cars.’
3. Strong Multimedia Support
o FHD+ Display Support: Compatible with mainstream in-car systems’ 1080p screens, delivering crisp and detailed visuals.
o 4K Codec Capability: Can fully support the playback and recording of high-definition 360° surround-view imagery and high-definition dashcam videos, with no pressure for future upgrades to even higher-resolution cameras.
4. Integrated NPU Unit
o Provides basic AI computing power, enabling fundamental AI functions such as offline voice recognition and control (e.g., ‘Hello, XX’ wake word and commands) and driver status monitoring (DMS, e.g., fatigue driving, distraction alerts), enhancing the intelligence level of the in-vehicle system.
Conclusion: The Unisoc 7862S (T740) is a powerful 5G chip, but its ‘consumer-grade’ nature makes it less ideal as a master control chip for in-vehicle infotainment systems, especially in the pre-installation market.

The Unisoc 7865 is essentially the Unisoc Tangula T760 chip.
Chip Overview: Tangula T760 (Unisoc 7865)
· Official Model: Unisoc Tangula T760 (Tiger T760). ‘7865’ is one of its commercial codes.
· Process Technology: Utilizes an advanced 6nm EUV process, delivering excellent power efficiency and representing one of Unisoc’s most advanced manufacturing technologies to date.
· CPU Architecture: Octa-core CPU consisting of four high-performance Arm Cortex-A76 cores (2.2GHz) and four power-efficient Arm Cortex-A55 cores (2.0GHz). This configuration offers a performance upgrade compared to the T740 (A75+A55).
· GPU: Integrates an Arm Mali-G57 MC4 GPU, providing mainstream-level graphics processing capabilities.
· Key Highlight: Features an integrated 5G modem supporting NSA/SA dual-mode 5G networks and Sub-6GHz bands, with a downlink peak rate of up to 3.67Gbps.
· AI: Equipped with an NPU (Neural Processing Unit) delivering 4.8 TOPS of computing power, making AI performance a significant selling point.
· Multimedia: Supports up to 4K@30fps video encoding/decoding and display output with a maximum resolution of 2520×1080 (FHD+). Some sources indicate support for even higher resolutions.
Disadvantages (Weaknesses and Challenges) – Core Issues Persist
1. The Fundamental Challenge: Non-Automotive-Grade Certification
· Reliability Risks: Like the T740, the T760 remains essentially a commercial-grade chip and has not been publicly announced as compliant with AEC-Q100 automotive certification. This is the most significant barrier to its adoption in automotive systems.
· Questionable Environmental Adaptability: Commercial-grade chips cannot fully meet the stringent automotive requirements for operating temperature, vibration resistance, electromagnetic interference immunity, long-term stability, and lifespan (yield and consistency) — such as the demanding -40°C to 85°C+ range. In extreme conditions (e.g., severe cold or intense heat), there is a risk of performance instability or failure, representing a safety hazard unacceptable in the pre-installation market.
2. Lack of Functional Safety
· It does not support ASIL (Automotive Safety Integrity Level) standards such as ISO 26262. This means it cannot be used to control any safety-critical vehicle functions (e.g., braking, steering, instrument clusters) and can only serve as the main controller for the infotainment system (IVI). Moreover, its own failures are not accounted for within the vehicle’s functional safety architecture.
3. Software and Ecosystem Barriers
· Absence of Automotive Software Stack: The chip manufacturer may not provide a complete BSP (Board Support Package) or middleware tailored for the automotive industry. Support for automotive bus protocols such as CAN FD, Automotive Ethernet, and AutoSAR requires additional adaptation by developers, resulting in high difficulty, cost, and extended development cycles.
· Uncertain Long-Term Support: Automotive projects have long lifecycles, requiring chip supply guarantees for over 10 years. The rapid iteration cycle of commercial-grade chips introduces uncertainty regarding long-term availability and software maintenance.



